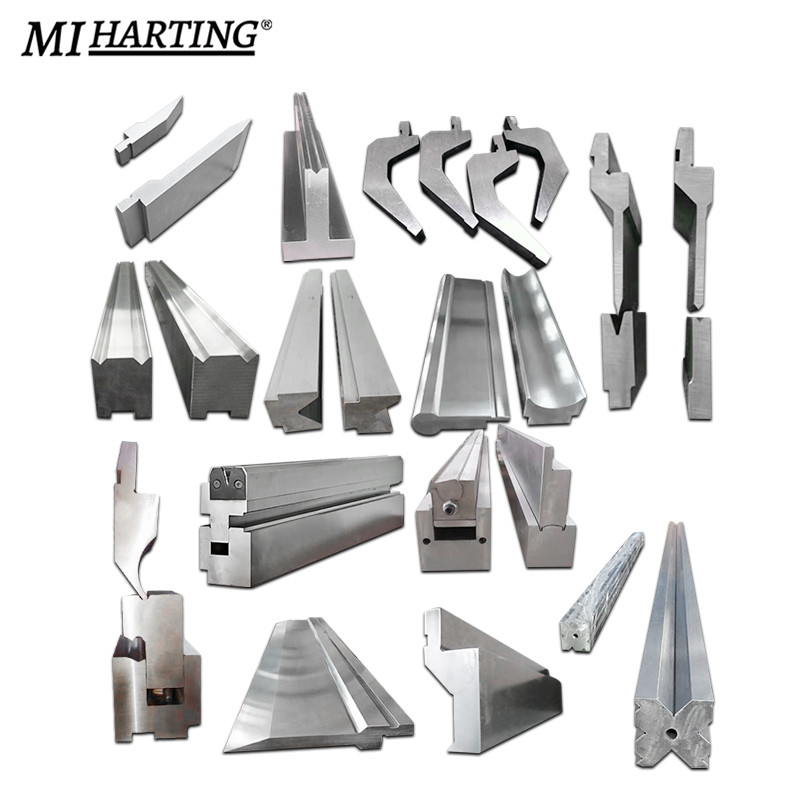
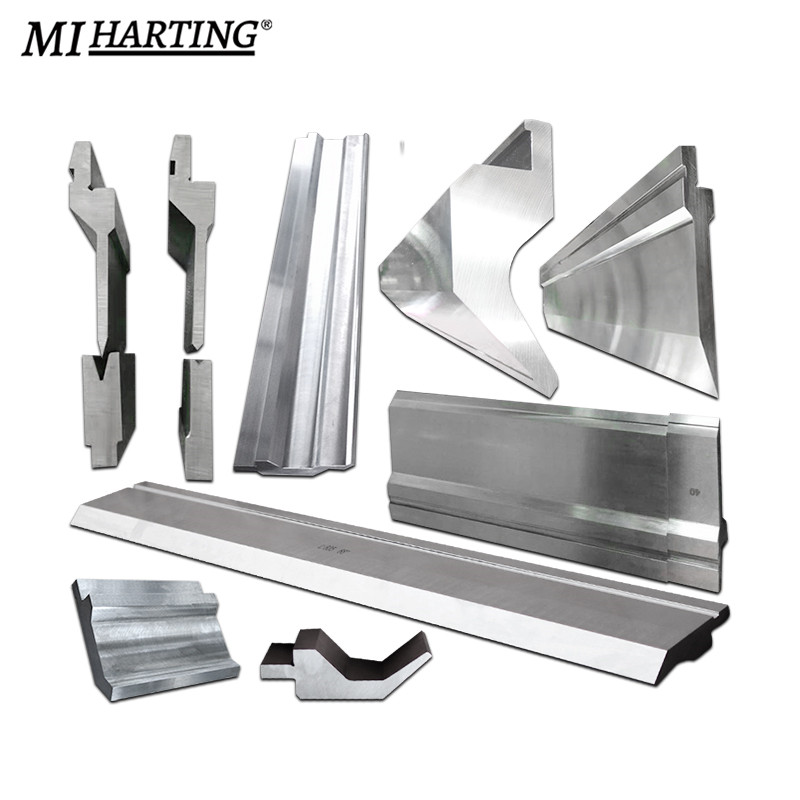
Common Types of Press Brake Tools:
- FLATTENING PRESS BRAKE DIE
The flattening press brake die is a specialized tool used in press brake machines to flatten bent metal sheets or plates. It consists of a die set with a flat surface that exerts uniform pressure on the material being processed. This die is typically used to remove unwanted bends, twists, or warping from the metal, ensuring it becomes flat and smooth. It helps achieve precise flatness by evenly distributing the force across the entire surface.
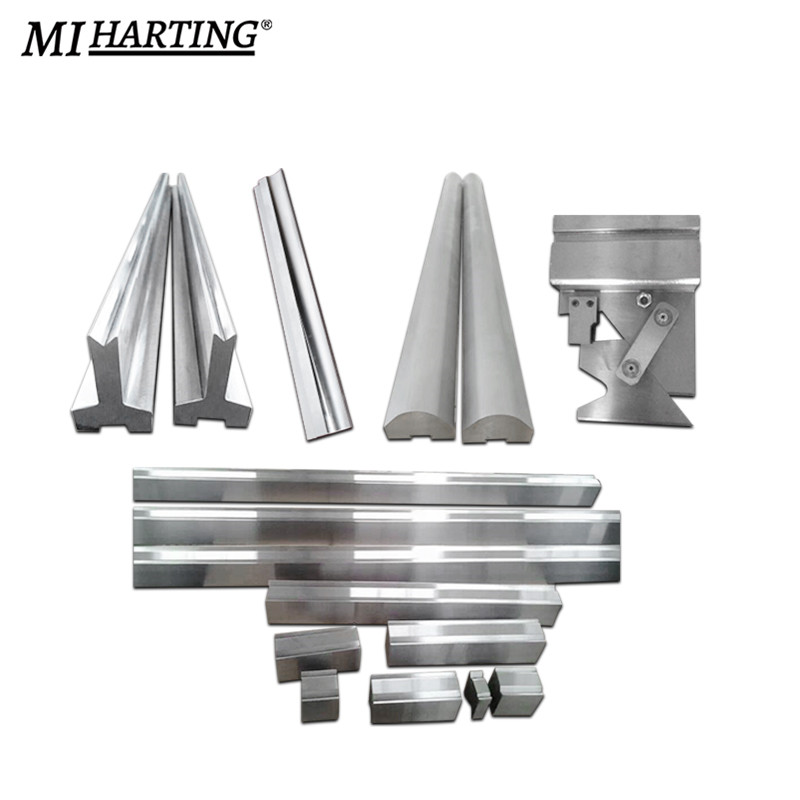



Press brake arc refers to the technique of bending metal sheets or plates into an arc or curved shape using a press brake machine. It involves utilizing a die set with a matching radius to create the desired curved profile. By adjusting the bending angle and applying controlled force, the metal is gradually shaped into the desired arc. Press brake arcs are commonly used in various applications, such as forming cylindrical parts, curved architectural components, or round ductwork.


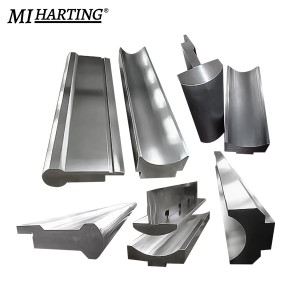
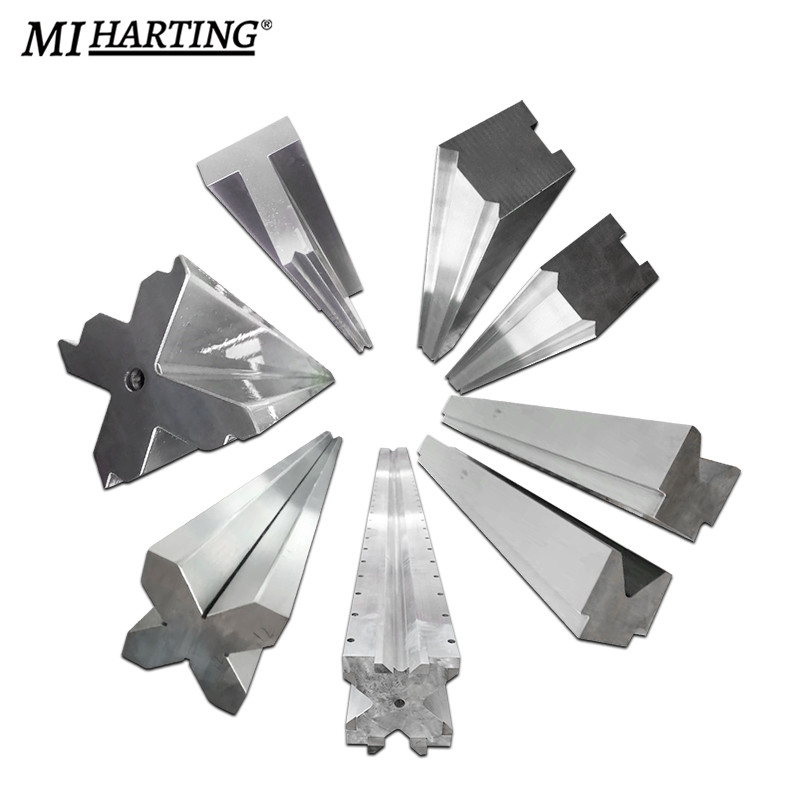
Press brake multi-V tooling is a versatile set of tools used in press brake machines for achieving different bending angles and shapes. It consists of a range of V-shaped dies with varying widths, depths, and angles. Operators can select the appropriate V-shaped die based on the desired bend specification. These tooling sets provide flexibility in creating a wide array of bends, including sharp angles, obtuse angles, channels, flanges, and more. The interchangeable nature of the dies allows for quick adjustments and efficient production.


Application scenarios of Press Brake Tools:
FLATTENING PRESS BRAKE DIE:
- The flattening press brake die is commonly used in sheet metal fabrication to remove unwanted bends, twists, or warping from bent metal sheets or plates. It finds applications in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, appliance manufacturing, and metalworking. This die is particularly useful for correcting parts that have undergone previous bending processes and need to be flattened before further processing or assembly.
PRESS BRAKE ARC:
- 1. Automotive Industry: Press brake arcs are used to create curved body panels, fenders, and structural components in the automotive industry.
- 2. HVAC Industry: Curved ductwork, ventilation pipes, and air handling components often require the use of press brake arcs.
- 3. Architectural Industry: Press brake arcs are used to form curved architectural elements such as handrails, balustrades, decorative panels, and curved facades.
- 4. Furniture Industry: Curved metal parts like chair frames, table bases, and decorative features can be produced using press brake arcs.
PRESS BRAKE MULTI-V TOOLING:
- 1. Metal Enclosures: Press brake multi-V tooling is used to create flanges, channels, and corners in metal enclosures for electrical cabinets, control panels, and machinery housings.
-
2. Brackets and Mounting Plates: Multi-V tooling allows for precise bending of brackets, mounting plates, and angle components used in various industries.
-
3. Structural Components: Press brake multi-V tooling is employed in the production of structural components such as beams, angles, and supports with different bend angles and shapes.
-
4. Equipment and Machinery: Many machinery and equipment manufacturers rely on press brake multi-V tooling to fabricate parts with specific shapes, angles, and flanges required for assembly and function.
When selecting bending machine tools, there are several key points to consider:
- 1. Material Compatibility: Determine if the bending machine tool is suitable for the specific type and thickness of material you will be working with. Different materials, such as steel, aluminum, or stainless steel, have varying hardness and ductility, which may require different tooling configurations.
- 2. Bending Capacity: Consider the maximum bending capacity of the tool. This includes factors such as the maximum thickness and width of the material that can be effectively bent. Ensure the tool can handle the size and thickness requirements of your intended applications.
- 3. Tooling Options: Assess the range of tooling options available for the bending machine. Different tooling sets allow for various bend angles, shapes, and profiles. Consider the versatility and flexibility offered by the available tooling options to meet your specific bending needs.
- 4. Bending Accuracy and Precision: Look for bending machine tools that offer high accuracy and precision in achieving desired bend angles and dimensions. The tool should provide reliable repeatability, ensuring consistent results across multiple bends.
- 5. Ease of Tool Change: Consider the ease and efficiency of tool changeovers. Quick and simple tool changes enhance productivity and reduce downtime. Look for tooling systems that facilitate easy and rapid interchangeability of dies and punches.
- 6. Machine Compatibility: Ensure that the bending machine tools are compatible with the specific type and model of bending machine you have or plan to acquire. Confirm that the tooling system is designed to fit and work seamlessly with your machine.
- 7. Supplier Support and Service: Evaluate the reputation and support provided by the tooling supplier. Look for a reputable supplier who offers technical assistance, training, and responsive customer service to address any issues or inquiries that may arise during tooling selection or usage.
The operating techniques and safety precautions for press brake operators when using Press Brake Tools:
- 1. Use the correct tool setup. Ensure that the chosen tools match the material type, thickness, and desired bend angle.
- 2. Determine the proper pressure and backgauge position. Adjusting the pressure and backgauge position can improve bending accuracy and material forming quality.
- 3. Check and adjust the position of the workpiece. Before starting the bending process, adjust the position of the workpiece to fit the selected tools and ensure it is in the correct location and orientation.
- 4. Perform test bends. Conducting test bends before actual production can help identify and correct any issues or errors.
- 5. Regularly inspect and maintain the machine and tools. Keep them clean and perform maintenance according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- 6. Wear personal protective equipment. This includes a helmet, safety goggles, gloves, ear protection, non-slip shoes, etc.
- 7. Follow safety regulations for the machine and tools. Ensure that you are familiar with and adhere to the guidelines for safe operation and proper use of the press brake equipment and tools.
- 8. Properly clamp and adjust. When clamping and adjusting the tools, avoid placing hands or other body parts in the hazardous areas of the machine.
- 9. Be mindful of the working environment and surrounding area. Keep the workplace clean and tidy to prevent tripping and slipping hazards, and ensure that there are no dangerous objects in the work area.
- 10. Manage materials and waste properly. Correctly handle and store materials, as well as clean up debris and waste, are important steps in ensuring safety.
Here are some tips for the maintenance and upkeep of Press Brake Tools:
-
1. Keep it clean: Regularly clean the surface and internal parts of the tools to prevent rust, corrosion, and damage.
-
2. Check and replace machine oil and lubricants: Ensure that the oils and lubricants are clean and have the proper viscosity to avoid damage caused by oil or lubricant-related issues.
-
3. Periodically inspect the tools for wear: Replace heavily worn tools promptly to maintain accuracy and longevity.
-
4. Grind and recondition the punch and die: This helps repair any damage, wear, or deformation and restores the accuracy of notches and bends.
-
5. Ensure the tightness of all bolts and fasteners: Loose or missing bolts and fasteners can cause tool displacement and deformation.
-
6. Replace components periodically as per manufacturer's guidelines: Parts like springs, blades, hydraulic seals, etc., need regular replacement to ensure proper machine operation.






